Aleta ransomware removal: how to decrypt .aleta virus files

The ubiquitous ransomware epidemic continues to dodge conventional defenses when plaguing users around the globe. The theme of code inheritance is in vogue with cyber extortionists for a reason. This way, they fine-tune their malicious programs to make them increasingly elusive and more difficult to crack. That’s what happened in early July 2017 with the emergence of a new BTCWare virus spinoff called the Aleta ransomware.
Table of Contents
What is the Aleta ransomware?
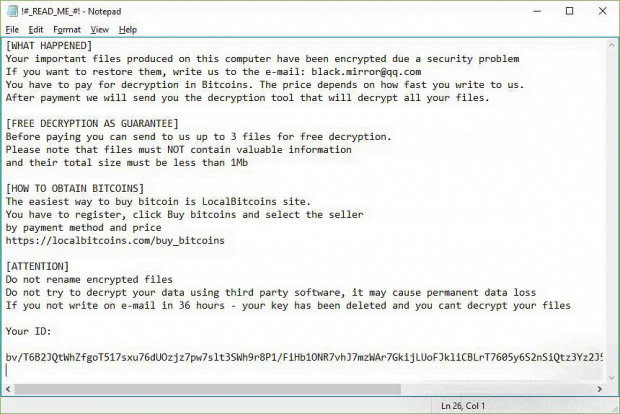
As it has been mentioned, the Aleta ransomware is not an independently created strain. Its roots reach back to one of the most widespread file-encrypting malware families generically dubbed BTCWare. The revamped infection got some fresh makeup, namely the .aleta file extension concatenated to hostage entries and ransom notes named !#_READ_ME_#!.inf opening up with Notepad. The offending code sticks with the following file tweaking format: [original filename].[email address].aleta, so it’s a no-brainer to work out which data items have been ransomed. The email address preceding the strain-specific extension may be one of the following: darkwaiderr@cock.li, black.mirror@qq.com, blacklandfat@qq.com, roggers@bigmir.net, realsapport@bigmir.net, mail@aleta.cc, help@cryptmaster.info, payfordecrypt@qq.com, to name a few.
As a result of such a file-skewing routine, a document with the filename Essay.docx will change to something like Essay.docx.[black.mirror@qq.com].aleta, where the email string may vary. This change is only the tip of the iceberg, though. A much worse thing is that none of these files can be accessed – opened or edited – until the victim meets the threat actors’ demands. The cryptographic aspect of the Aleta ransomware circles around the use of two ciphers, AES-256 and RSA-1024, which blend crypto symmetry and asymmetry into a rock-solid fusion. It’s with the onset of this particular BTCWare edition that the crooks in charge have started utilizing the new uncrackable algorithmic take on victims’ important files. Previous variants had a flaw in this regard, which allowed researchers to decrypt them. Unfortunately, this has changed with Aleta.
The attack chain makes this particular ransomware lineage stand out from the vast majority. Rather than infiltrate computers via trojanized spam attachments or exploits, the malicious process is executed manually. What makes such onslaughts possible is users’ unwise security practices. The breach takes place through remote desktop services that aren’t properly protected with hard-to-guess access credentials. In other words, the Aleta virus comes in via compromised RDP connections. Users should be doing a better job applying the corresponding authentication these days. Since RDP is a clever ransomware attack vector, perhaps it’s a good idea to disable it when not in use.
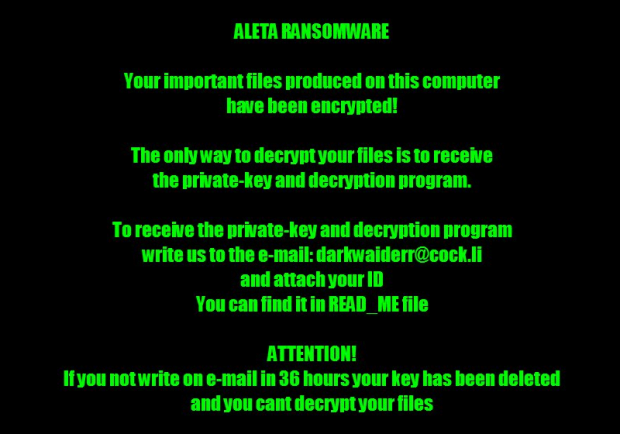
Having made it on board, Aleta scours the machine and mapped network drives for potentially valuable files. Each detected entry is subject to encryption. Then, the ransomware modifies the desktop wallpaper to the image above that says, “Aleta ransomware – Your important files produced on this computer have been encrypted.” The entirety of attack information and ransom demands is explicated in the above-mentioned !#_READ_ME_#!.inf document. The victim is instructed to reach the felons over email, attaching their personal ID to the message. The deadline to do it is 36 hours. The criminals will then send specific demands in response – they want 0.5 Bitcoin (about $1,100) for the private key. Before even considering the ransom option, though, be sure to try the recovery steps below.
Aleta file automatic removal
Extermination of this ransomware can be efficiently accomplished with reliable security software. Sticking to the automatic cleanup technique ensures that all components of the infection get thoroughly wiped from your system.
1. Download recommended security utility and get your PC checked for malicious objects by selecting the Start Computer Scan option
Download Aleta ransomware remover
2. The scan will come up with a list of detected items. Click Fix Threats to get the file and related infections removed from your system. Completing this phase of the cleanup process is most likely to lead to complete eradication of the plague proper. Now you are facing a bigger challenge – try and get your data back.
Methods to restore files encrypted by Aleta file
Workaround 1: Use file recovery software
It’s important to know that the Aleta file creates copies of your files and encrypts them. In the meanwhile, the original files get deleted. There are applications out there that can restore the removed data. You can utilize tools like Stellar Data Recovery for this purpose. The newest version of the file under consideration tends to apply secure deletion with several overwrites, but in any case this method is worth a try.
Download Stellar Data Recovery Professional
Workaround 2: Make use of backups
First and foremost, this is a great way of recovering your files. It’s only applicable, though, if you have been backing up the information stored on your machine. If so, do not fail to benefit from your forethought.
Workaround 3: Use Shadow Volume Copies
In case you didn’t know, the operating system creates so-called Shadow Volume Copies of every file as long as System Restore is activated on the computer. As restore points are created at specified intervals, snapshots of files as they appear at that moment are generated as well. Be advised this method does not ensure the recovery of the latest versions of your files. It’s certainly worth a shot though. This workflow is doable in two ways: manually and through the use of an automatic solution. Let’s first take a look at the manual process.
-
Use the Previous Versions feature
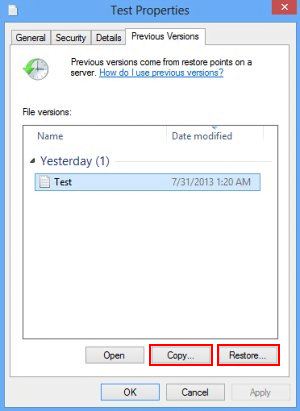
The Windows OS provides a built-in option of recovering previous versions of files. It can also be applied to folders. Just right-click on a file or folder, select Properties and hit the tab named Previous Versions. Within the versions area, you will see the list of backed up copies of the file / folder, with the respective time and date indication. Select the latest entry and click Copy if you wish to restore the object to a new location that you can specify. If you click the Restore button, the item will be restored to its original location.

-
Apply Shadow Explorer tool
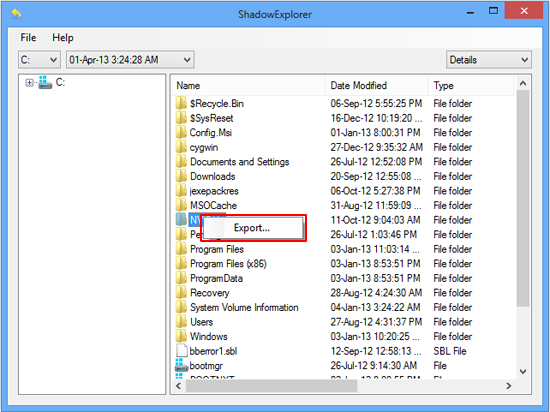
This workflow allows restoring previous versions of files and folders in an automatic mode rather than by hand. To do this, download and install the Shadow Explorer application. After you run it, select the drive name and the date that the file versions were created. Right-click on the folder or file of interest and select the Export option. Then simply specify the location to which the data should be restored.

Verify whether Aleta file has been completely removed
Again, ransomware removal alone does not lead to the decryption of your personal files. The data restore methods highlighted above may or may not do the trick, but the file itself does not belong inside your computer. Incidentally, it often comes with other file, which is why it definitely makes sense to repeatedly scan the system with automatic security software in order to make sure no harmful remnants of this file and associated threats are left inside Windows Registry and other locations.
Posted in: KnowledgeBase
Leave a Comment (0) ↓